| Want to send this page or a link to a friend? Click on mail at the top of this window. |
More Special Reports |
| Posted September 9, 2009 |
| National |
| Overspending on Debit Cards |
|
Is Painful, but Not for Banks |
 |
|
LAURA PEDRICK FOR THE NEW YORK TIMES |
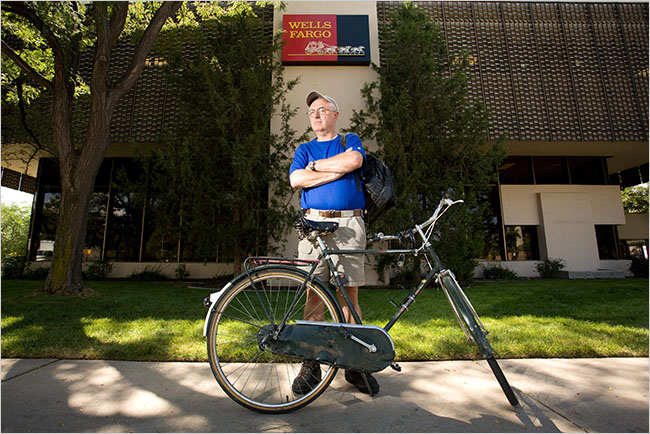
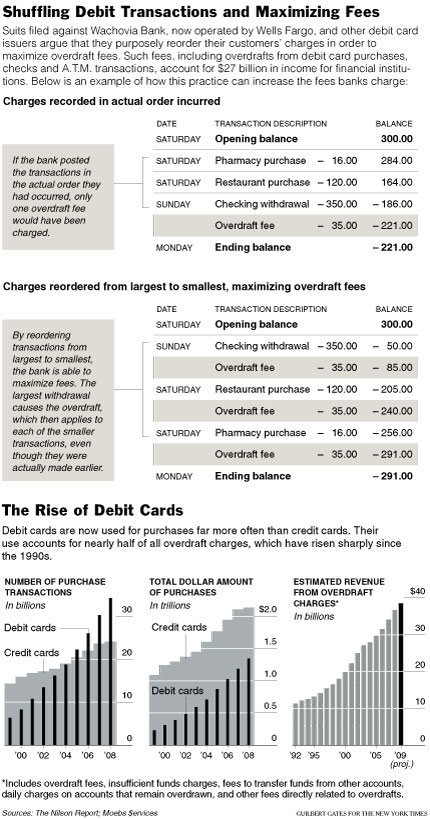
| above, has filed a lawsuit against Wachovia Bank. The suit charges that the bank reorders debit card transactions in order to maximize the overdraft fees they can charge. |
|
By RON LIEBER |
|
and ANDREW MARTIN |
 |
|
MATTHEW STAVER FOR THE NEW YORK TIMES |
| Peter Means's bank charged him seven $34 fees to cover seven purchases when there was not enough cash in his account, notifying him only afterward. |
 |
|
|
|
| A Source of Easy Money |
| 'I Can't Afford That' |
| The Debate in Washington |
| Wehaitians.com, the scholarly journal of democracy and human rights |
| More from wehaitians.com |